Refind Boot Manager For Mac

Abstract As a network and security architect, I sometimes need to test security and network policies using different OS. A virtual machine can help but what if you need to test policies against physical hardware?
I have a 250GB SSD, and I’m going to allocate:. 50GB for OS X. 50GB for Windows. 150GB for Ubuntu Linux 16.04, my preferred OS I made lot of tests to make everything working fine, so be sure you follow the steps below carefully. Mind that you’ll need three USB keys:. Windows 10 installation.
Windows 10 recovery. Ubuntu 16.04 installation Install or prepare OS X If you have a OSX installed on a single partition, filling the whole disk, go to the next step below in this paragraph. Otherwise, I suggest to reinstall OS X:. power off your Mac;. keep pressing command + R while you power on your Mac (release when the apple disappear) and boot into macOS Recovery mode;. OS X Utilities will be loaded:.
open Disk Utility, select your main disk and press erase (do that more than once, if first attempt fails);. name your new partition OSX;. quit Disk Utility;. open Install OS X and install it.
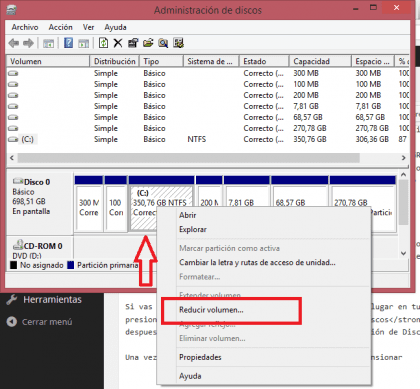
When installation is completed, consider to upgrade your OS X to latest version. After that:.;.;.;. and unpack it;. open BootCamp and prepare the first USB key for Windows installation media;. start UNetbootin and prepare also the second USB key for Ubuntu installation media;. download refind and unpack it;.
open Disk Utility;. create another partition, leaving 50GB for OS X partition;. power off your Mac.
Install Windows At the end of this section, you will have a dual boot Mac: OS X and Windows 10. You can boot one OS using Startup Manager or via Boot Camp. Let’s begin:. insert the Windows installation USB key;. power on holding option/alt to open the Startup Manager;.
boot from Windows installation USB key;. in the disk manager, remove the non OS X partition (remove the second one, the bigger one);. create a new 50GB partition and install Windows on it;. be sure Boot Camp package is installed too (it contains Mac drivers for Windows);. create a Windows USB recovery drive;.
power off your Mac. Installing ReFind At the end of this section, we’ll install a new bootloader to better manage a multi OS Mac. Let’s begin:. keep pressing command + R while you power on your Mac (release when the apple disappear) and boot into macOS Recovery mode;. OS X Utilities will be loaded;.
open Disk Utility and mount OS X partition; Image. quit Disk Utility;. open a terminal and install rEFInd (continue even if you got a warning). # cd /Volumes/OSX/Users/andrea/Destkop/refind-0.10.2 #./refind-install.
power off your Mac. Install Ubuntu Linux At the end of this section, you will have a dual boot Mac: OS X and Ubuntu Linux 16.04. Windows 10 will be broken by Ubuntu installation.
Let’s begin:. insert the Ubuntu installation USB key;.
power on holding option/alt to open the Startup Manager;. boot from Ubuntu installation USB key;.
install Ubuntu using the free space (about 150GB);. power off your Mac.
Fixing Windows 10 boot (0xc000000e error) After Ubuntu installation, Windows 10 won’t boot anymore. Boot will will fail with 0xc000000e error.
Fixing that was the hardest part of this journey. Let’s see how to fix it:. power on your Mac and boot Ubuntu;. login, open a shell with administrative privileges;. edit /boot/efi/EFI/refind/refind.conf and include gptsync. Showtools shell, gdisk, memtest, moktool, applerecovery, windowsrecovery, about, reboot, exit, firmware, fwupdate, gptsync.
reboot your Mac and select Hybrid MBR tool ( gptsync) from rEFInd boot loader;. gptsync should detect four partitions:. EFI PRotective. NTFS/HPFS.
Linux. Linux swap / Solaris. confirm gptsync you want to sync MBR and GPT;.
power off your Mac;. insert the Windows USB recovery drive;.
power on holding option/alt to open the Startup Manager;. boot from Windows USB recovery drive;. open a command prompt and type.
Installing elementary OS alongside macOS Table of Contents. This guide makes a few assumptions about the Mac you're using. Before we you begin, make sure: Your Mac only has macOS installed on it. If you have an existing install of elementary OS or Windows on your computer, this guide may not fully apply to you.
You're running OS X 10.11 El Capitan or macOS 10.12 Sierra This guide is written with recent versions of macOS in mind. If you're using an older version, things might be different, so bear that in mind.
Your Mac is relatively new (2012 or later) Your Mac must not have a Core 2 duo or Solo (or older) processor. Only the past couple few years of Macs (which have 64-bit EFI) are supported. Your Mac is not a 2015/2016 MacBook or 2016 MacBook Pro At the time of writing (December 2016), these very new models have limited functionality under elementary OS.
At least 15GB of extra disk space on your Mac. iso. Boot Manager. at least 2GB capacity.
Lots of patience! NOTE: For those who don't know this, a dollar sign ( $) indicates that you type the command into a Terminal window. You do not copy the dollar sign:-) Prep Your Mac Hard Drive. Back your computer up. No, really! Make sure you have a backup, and make sure to test that it works.
This procedure has been tested multiple times, but there's still a chance something could go wrong and you could lose data. On macOS, is a great option for backing your computer up.
Shrink your macOS partition to make room for elementary OS. At least 30 GB is a reasonable minimum. If you plan on using elementary OS as your primary OS, you'll want to give it much more, of course. Once you decide what size you want to resize your macOS partition down to, you can resize it with this command: $ diskutil cs resizeStack / XXXg, where XXX is the desired number of GB your macOS partition will be resized down to. For example, if your Mac has a 500 GB internal hard drive, you might decide to allocate 300 GB for macOS, and 200 GB for elementary OS. You'd then issue this command: $ diskutil cs resizeStack / 300g. Get elementary OS.
Download the iso from. Verify the download by running this command from terminal:. shasum -a 256 /Downloads/elementaryos-0.4-stable-amd1.iso. Should give you the result 8035e0a2fbc977d931af22dcefb77ed6fe8a43e2cb345f13e629cf. Create a Bootable USB using. More details on the Install elementary OS.
Shut off your Mac and plug in the USB flash drive you created with elementary OS on it. Holding down the option key on your keyboard, press the power button to turn on your computer. From the boot manager screen that appears, choose elementary OS. After choosing to boot elementary OS, you'll be given a few options as to how to boot the installer. Choose Try Elementary OS. Once elementary OS finishes booting up, open Terminal and run $ ubiquity -b. This will launch the graphical elementary OS installer.
When the installer asks about partitioning, make sure you choose Something Else. Note for advanced users: the -b flag tells the installer to install without installing the GRUB boot-loader. This guide makes use of, which allows a capable boot manager (such as rEFInd, which we'll set up later) to launch the Linux kernel directly, without an intermediary boot-loader (e.g. You should see some free space at the end your hard drive partition list ( /dev/sda), about the size you freed up when you shrunk your macOS partition. Choose this free space, and format it as Ext4 and set its mount point to /. Choose Apply, and finish installing elementary OS.
Install reFInd Boot Manager. Restart your computer and boot back into macOS. At this point, elementary OS is installed, but you can't boot into it yet, because you haven't installed a boot manager.
Refind Boot Manager Download For Mac
That's the next step!. the rEFInd boot manager and unzip it. Drag the unzipped folder onto your desktop.
Turn off your Mac. Boot into Recovery Mode by holding down ⌘ + R while turning on your Mac. Once in Recovery Mode, open Disk Utility.
Refind Download
Choose your macOS partition and click Mount in the toolbar to mount it. Quit Disk Utility and open Terminal. cd into the directory where you unzipped rEFInd, which will probably be something like /Volumes/Macintosh HD/Users/jane/Desktop/refind., if your macOS username was jane. Install rEFInd ( $./refind-install).
Reboot your Mac. You should now see the rEFInd menu, which options to boot elementary OS and macOS.
You're all set. You can install a to make it look nicer, and there's many options for customizing rEFInd's behavior too. Here's what my setup looks like: These are optional tweaks that will help you feel more are home. Create macOS like keyboard bindings plugin to help alleviate eye-strain make your bash shell awesome package manager for linux My Wi-Fi isn't working Sometimes Wi-Fi might not work out-of-the-box because the necessary driver isn't installed. In some cases, you'll be able to install them manually. Somehow get a temporary internet connection, e.g. Via your smartphone's USB or Bluetooth tethering function or a (Thunderbolt ethernet works well with 0.4.1 Loki).

Run $ sudo apt install bcmwl-kernel-source to install the driver and its dependencies. It takes 30 seconds for the rEFInd menu to show up.
This is a known compatibility issue with rEFInd and some Mac hardware models. If you experience this problem, try the following steps:. Mount your EFI System Partition (ESP), which is where rEFInd is installed. ( $ sudo./mountesp). Rename the refind directory ( $ mv /Volumes/ESP/EFI/refind /Volumes/ESP/EFI/BOOT). Rename the refind EFI blob ( $ mv /Volumes/ESP/EFI/BOOT/refindx64.efi /Volumes/ESP/EFI/BOOT/bootx64.efi). Reboot and see if your problem is fixed.